Bout of Jaundice Can I Ever Drink Again?
In jaundice, the pare and whites of the eyes wait yellowish. Jaundice occurs when in that location is as well much bilirubin (a xanthous pigment) in the blood—a condition chosen hyperbilirubinemia.
Bilirubin is formed when hemoglobin (the part of red blood cells that carries oxygen) is cleaved down as role of the normal process of recycling old or damaged red blood cells. Bilirubin is carried in the bloodstream to the liver, where it binds with bile (the digestive juice produced by the liver). Bilirubin is and so moved through the bile ducts into the digestive tract, and so that information technology can exist eliminated from the body. Almost bilirubin is eliminated in stool, but a small amount is eliminated in urine. If bilirubin cannot be moved through the liver and bile ducts speedily enough, information technology builds upwards in the blood and is deposited in the skin. The result is jaundice.
Many people with jaundice also take dark urine and calorie-free-colored stool. These changes occur when a blockage or other problem prevents bilirubin from being eliminated in stool, causing more bilirubin to be eliminated in urine.
Also, many disorders that cause jaundice, particularly severe liver disease, cause other symptoms or serious problems. In people with liver affliction, these symptoms may include nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain, and small spiderlike blood vessels that are visible in the peel (spider angiomas). Men may have enlarged breasts, shrunken testes, and pubic hair that grows as information technology does in women.
Serious problems caused by liver disease can include
If people eat big amounts of food rich in beta-carotene (such every bit carrots, squash, and some melons), their skin may expect slightly yellowish, just their eyes do not plow xanthous. This status is non jaundice and is unrelated to liver illness.
Jaundice in adults has many causes. Nearly causes involve disorders and drugs that
-
Damage the liver
-
Interfere with the menstruum of bile
-
Trigger the destruction of red claret cells (hemolysis), thus producing more bilirubin than the liver can handle
View of the Liver and Gallbladder
The most common causes of jaundice are
Less common causes of jaundice include hereditary disorders that interfere with how the body processes bilirubin. They include Gilbert syndrome and other, less common disorders such every bit Dubin-Johnson syndrome. In Gilbert syndrome, bilirubin levels are slightly increased but usually not enough to crusade jaundice. This disorder is about often detected during routine screening tests in young adults. It causes no other symptoms and no issues.
In people with jaundice, the following symptoms are cause for business concern:
-
Astringent abdominal pain and tenderness
-
Changes in mental function, such equally drowsiness, agitation, or confusion
-
Blood in stool or tarry black stool
-
Claret in vomit
-
Fever
-
A tendency to trample or to bleed easily, sometimes resulting in a blood-red royal rash of tiny dots or larger splotches (which indicate bleeding in the skin)
If people have any warning signs, they should run into a md as soon as possible. People with no warning signs should meet a medico inside a few days.
Doctors ask when the jaundice started and how long it has been present. They also ask when urine started to look nighttime (which normally occurs before jaundice develops). People are asked near other symptoms, such as itching, fatigue, changes in stool, and abdominal pain. Doctors are specially interested in symptoms that suggest a serious cause. For instance, sudden loss of appetite, nausea, airsickness, hurting in the belly, and fever suggest hepatitis, peculiarly in immature people and people with risk factors for hepatitis. Fever and severe, abiding hurting in the upper right office of the abdomen suggest acute cholangitis (infection of the bile ducts), commonly in people with a blockage in a bile duct. Acute cholangitis is considered a medical emergency.
Doctors enquire people whether they have had liver disorders, whether they take had surgery that involved the bile ducts, and whether they take whatever drugs that can cause jaundice (for instance, the prescription drugs amoxicillin/clavulanate, chlorpromazine, azathioprine, and oral contraceptives; alcohol; over-the-counter drugs; medicinal herbs; and other herbal products such every bit teas). Knowing whether family members accept as well had jaundice or other liver disorders can help doctors identify hereditary liver disorders.
-
Working at a twenty-four hours care heart
-
Living in or working at an establishment with long-term residents, such as a mental health intendance facility, prison, or long-term care facility
-
Living in or traveling to an expanse where hepatitis is widespread
-
Participating in anal sex activity
-
Eating raw shellfish
-
Injecting illegal or recreational drugs
-
Having hemodialysis
-
Sharing razor blades or toothbrushes
-
Getting a tattoo or body piercing
-
Working in a wellness care facility without being vaccinated confronting hepatitis
-
Having had a blood transfusion earlier 1992
-
Having sex with someone who has hepatitis
-
Having been born between 1945 and 1965
During the physical examination, doctors look for signs of serious disorders (such as fever, very low blood pressure, and a rapid eye charge per unit) and for signs that liver role is greatly impaired (such every bit easy bruising, a rash of tiny dots or splotches, or changes in mental function). They gently printing on the abdomen to bank check for lumps, tenderness, swelling, and other abnormalities, such as an enlarged liver or spleen.
Tests include the following:
-
Blood tests to evaluate how well the liver is performance and whether it is damaged (liver tests)
-
Commonly imaging tests such as ultrasonography Ultrasonography Imaging tests of the liver, gallbladder, and biliary tract include ultrasonography, radionuclide scanning, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography... read more , computed tomography Computed Tomography Imaging tests of the liver, gallbladder, and biliary tract include ultrasonography, radionuclide scanning, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography... read more (CT), or magnetic resonance imaging Magnetic Resonance Imaging Imaging tests of the liver, gallbladder, and biliary tract include ultrasonography, radionuclide scanning, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography... read more (MRI)
Other blood tests are done based on the disorder doctors suspect and the results of the examination and the initial tests. They may include
-
Tests to appraise the blood's ability to clot (prothrombin fourth dimension and partial thromboplastin time)
-
Tests to bank check for hepatitis viruses or abnormal antibodies (due to autoimmune disorders)
-
A complete claret count
-
Blood cultures to cheque for infection of the bloodstream
-
Examination of a blood sample nether a microscope to cheque for excessive devastation of red blood cells
If imaging is needed, ultrasonography of the abdomen is oft done get-go. It tin usually discover blockages in the bile ducts. Alternatively, computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be done.
If ultrasonography shows a blockage in a bile duct, other tests may be needed to decide the crusade. Typically, magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP Magnetic Resonance Imaging Imaging tests of the liver, gallbladder, and biliary tract include ultrasonography, radionuclide scanning, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography... read more than ) or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Imaging tests of the liver, gallbladder, and biliary tract include ultrasonography, radionuclide scanning, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography... read more ) is used. MRCP is MRI of the bile and pancreatic ducts, washed with specialized techniques that brand the fluid in the ducts appear bright and the surrounding tissues appear nighttime. Thus, MRCP provides better images of the ducts than conventional MRI. For ERCP, a flexible viewing tube (endoscope) is inserted through the mouth and into the pocket-size intestine, and a radiopaque contrast agent is injected through the tube into the bile and pancreatic ducts. Then x-rays are taken. When available, MRCP is commonly preferred because it is merely as accurate and is safer. Just ERCP may be used considering information technology enables doctors to take a biopsy sample, remove a gallstone, or do other procedures.
-
Handling of cause
-
For itching, cholestyramine
Ordinarily, itching gradually disappears as the liver's status improves. If itching is bothersome, taking cholestyramine past mouth may help. Yet, cholestyramine is ineffective when a bile duct is completely blocked.
In older people, jaundice normally results from a blockage in the bile ducts, and the blockage is more probable to exist cancer. Doctors suspect that the blockage is cancer when older people have lost weight, have only mild itching, have no abdominal pain, and take a lump in the abdomen.
Jaundice is a yellow color of the skin and eyes acquired by having too much bilirubin in the blood.
Jaundice is caused past backlog bilirubin, which is formed when hemoglobin (the part of red blood cells that carries oxygen) is broken down equally role of the normal process of recycling erstwhile or damaged red blood cells. Commonly, the bilirubin is processed by the liver and excreted into the digestive tract. Bilirubin tin can build up in the blood and cause jaundice in the presence of certain kinds of liver damage (particularly from drinking too much alcohol Alcohol-Related Liver Disease Alcohol-related liver disease is liver damage caused past drinking too much alcohol for a long time. In general, the corporeality of alcohol consumed (how much, how often, and for how long) determines... read more 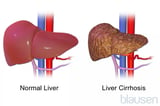 or from viral hepatitis Overview of Acute Viral Hepatitis Astute viral hepatitis is inflammation of the liver caused by infection with 1 of the five hepatitis viruses. In most people, the inflammation begins suddenly and lasts only a few weeks. Symptoms... read more ), blocked bile ducts Overview of Gallbladder and Bile Duct Disorders The liver produces bile, a dark-green yellow, thick, sticky fluid. Bile aids digestion past making cholesterol, fats, and fatty-soluble vitamins easier to absorb from the intestine. Bile also helps... read more
or from viral hepatitis Overview of Acute Viral Hepatitis Astute viral hepatitis is inflammation of the liver caused by infection with 1 of the five hepatitis viruses. In most people, the inflammation begins suddenly and lasts only a few weeks. Symptoms... read more ), blocked bile ducts Overview of Gallbladder and Bile Duct Disorders The liver produces bile, a dark-green yellow, thick, sticky fluid. Bile aids digestion past making cholesterol, fats, and fatty-soluble vitamins easier to absorb from the intestine. Bile also helps... read more 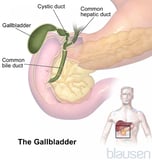 , or something that causes the cherry-red blood cells to break down faster than normal (hemolysis).
, or something that causes the cherry-red blood cells to break down faster than normal (hemolysis).
Doctors have to treat whatever is causing the jaundice. There is no specific treatment to make jaundice go away.
In addition to treating the crusade of the jaundice, doctors may give a drug, cholestyramine, to assist the itching caused by jaundice.
Many drugs tin crusade jaundice in adults, including acetaminophen, amiodarone, isoniazid, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), anabolic steroids, and a number of antibiotics.
Jaundice causes the skin and the whites of the optics to plow xanthous. The higher the bilirubin level, the yellower the peel. Severe jaundice usually also causes itching.
In good light, jaundice may be faintly visible in people whose bilirubin levels are between 2 and 3 mg/dL (34 to 51 micromol/L). A bilirubin level of 20 mg/dL (342 micromol/Fifty) can make the skin bright yellow, like a lemon.
-
If damage to the liver is severe, jaundice may be accompanied by serious bug, such as deterioration of brain function and a tendency to bleed or bruise.
-
Astute viral hepatitis is a mutual cause of jaundice, particularly in immature and otherwise healthy people.
-
People should run across a doctor promptly if they have jaundice so that the medico can bank check for serious causes.
-
Cholestyramine may aid relieve itching.
Source: https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/liver-and-gallbladder-disorders/manifestations-of-liver-disease/jaundice-in-adults
0 Response to "Bout of Jaundice Can I Ever Drink Again?"
Post a Comment